(Ms. Malvika Mahidhar)
We discussed about Egypt in this class. Starting with everyone saying whatever words they can associate with Egypt like Cleopatra, Mummy. Mummification, Tombs, Golden era, etc.
We saw images of some pottery with patterns on it and everyone was trying to decipher what it means.
There was a confusion between a sculpture and a statue so we were told to research on it in egyptian context. And also to research about the Egyptian symbols and what do they mean.
Egyptian symbols.

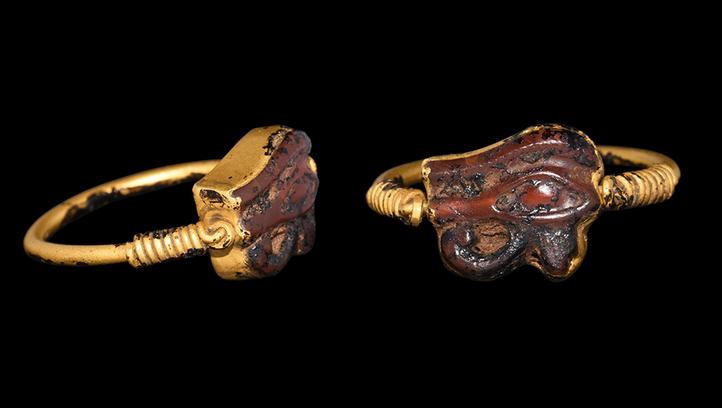
The Eye of Horus was a powerful symbol of protection and was incorporated into all sorts of jewelry to protect the wearer. It was also known as the “Eye of Ra,” a powerful destructive force linked with the fierce heat of the sun which was described as the “Daughter of Ra.” The eye was personified as the goddess Wadjet, who took the form of a cobra to protect the Pharaoh by being represented on his brow. This Eye of Horus is carved out of carnelian.
I thought this was a bracelet until i got to know the size. Before seeing this I thought the eye was made just for the sake of having some design because maybe they didn’t want plain looking, what I thought were bracelets.


The Hyksos were an were mixed Semitic-Asiatic peoples from West Asia who took over the eastern Nile Delta, ending the Thirteenth dynasty of Egypt and initiating the Second Intermediate Period (1650–1550 BC).
The Hyksos introduced the horse and chariot, the compound bow, improved battle axes, and advanced fortification techniques into Egypt. At Avaris,in the northeastern delta, they built their capital with a fortified camp over the remains of a Middle Kingdom town. Excavations since the 1960s have revealed a Canaanite-style temple, Palestinian-type burials, including horse burials, Palestinian types of pottery, quantities of their superior weapons, and a series of Minoan frescoes that demonstrate stylistic parallels to those of Knossos and Thera.
When i first looked at this object, it just looked like a stone with carvings on it and I thought it has something to do with fishery or a river because of the fish looking like symbols.

The Egyptian word ‘ankh’ means ‘life’. The hieroglyph with which this word is written, a cross with a loop on top, perhaps depicts a stylised sandal strap, with the loop being the ankle strap. Other people think that it is a penis sheath. As the symbol of life, it appears regularly in Egyptian art. In numerous reliefs, the king is being given (the symbol of) life by a god. An unusual and intimate way of depicting this may be seen in Amarna art – hands at the end of the Aten‘s rays are holding the sign to the noses of the king and his family. The sign is also common as an amulet, sometimes combined with a djed-pillar and/or a was-scepter. The Christian cross used in the Coptic church is based on the ankh sign.